Fundamental analysis
Introduction:
One of the most important steps that any trader or investor should take before starting to invest or trade in different markets, from stocks to forex and digital currency, is market analysis. Market analysis helps us discover important factors that affect the value of assets. There are different types of analysis; But two of the most popular ones are technical analysis and fundamental analysis. In this article, we examine fundamental analysis.
What is fundamental analysis?
Fundamental analysis, also known as fundamental analysis, is an approach to evaluate the intrinsic value of an asset or company. Intrinsic value is the real value that is estimated by analyzing the financial performance of the company or the performance of the asset in the market.
In fundamental analysis, we analyze external factors that affect the intrinsic value of an asset. Unlike technical analysis, which looks at historical price trends, fundamental analysis focuses on the underlying characteristics of the asset itself and the overall economic outlook. The purpose of this analysis is to discover the variables that affect the fair valuation of the asset so that the future performance of that asset can be accurately predicted. It is important to note that the intrinsic or fair value of an asset does not change overnight. Therefore, fundamental analysis can be helpful in identifying the fundamental characteristics of a company or asset.
Fundamental analysis is done at different levels. for example:
- At the organizational level, fundamental analysis includes the review of financial, management, business knowledge and competition data.
- At the industrial level, this analysis includes examining the forces of supply and demand for the products offered.
- In accounting and finance, fundamental analysis is a method of determining the intrinsic value of stocks, currencies or securities by examining many micro and macroeconomic factors.
Data used in fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis uses three data sets:
1. Historical data to check how the property has done in the past.
2. General information about the company, including announcements made by management or what others are saying about the company.
3. information that is not public; But it is useful. For example, we can mention how to manage crisis and difficult situations.
Different types of fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis is a combination of two main analysis:
- Qualitative analysis
- Quantitative analysis
Qualitative analysis
Qualitative fundamental analysis evaluates the nature and quality of a company or asset. The purpose of qualitative analysis is to evaluate the socio-economic position of the company. Some of the qualitative factors that we study in fundamental analysis are:
Business Model: The business model provides detailed information about the company and tells us how the business earns its revenue.
Company management: Smart investors look at company management before buying any stock or asset. Even the most powerful business models can fail if corporate governance is not strong. To conduct this research in fundamental analysis, the analyst may look at the board members’ resumes and investment behavior.
Company’s Articles of Association: An analysis of the company’s articles of association will give you an idea of the business’s policies and relations with shareholders. This helps create a deeper picture of the company’s ethics and performance.
Other factors that we examine in qualitative analysis include brand value, management decisions, financial performance of the company over a given period, goodwill, demand, consumer behavior, brand reputation in wider markets, and competitive advantage.
Qualitative analysis is done before quantitative analysis. After performing this analysis, you should have received the answers to the following questions:
- How efficient is the company operationally?
- How is the quality of the company’s management work?
- How is the brand value of this company determined?
- Does the company use proprietary technology?
- What initiatives does the company have for social responsibility?
- What is the company’s vision for the future?
After the answers to these questions are determined, you go to the next step.
Quantitative analysis
Fundamental analysis includes examining quantitative factors as well. Quantitative analysis is based solely on numbers and examines a company’s financial statements, reports, and the like. Thus, quantitative analysis is concerned with the measurable characteristics of a business. Important factors that should be examined in quantitative analysis are:
1. Checking financial statements
2. Annual report and presentation to investors
3. The growth of the company in a period of 3 to 5 years
4. Financial Ratio
1. Checking financial statements
The three main financial statements that a company presents to show its performance are:
Profit and Loss Statement
The profit and loss statement includes the company’s income and expenses for a certain period of time, for example, quarterly or annually. These documents show an insight into the profitability or loss of the company.
balance sheet
The balance sheet shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. On the balance sheet, at any point in time, a company’s total assets must always equal the company’s liabilities, including stockholders’ equity. that’s mean:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The balance sheet shows the company’s assets and liabilities. To determine whether a company is worth investing in, we look at the company’s total assets and total liabilities.
cash flow statement
The cash flow statement shows the inflow and outflow of money from the business and determines the financial health of the company or asset. The evaluation of these documents is very useful for investors; Because it shows a picture of the company’s daily performance.
2. Annual report and presentation to investors
The annual report is a comprehensive document that a company must provide to all its shareholders every year. This report includes the company’s operations throughout the year. You can determine the financial health of the company with the help of the annual report.
If you are a shareholder or investor, you should ask your business for financial/performance highlights, management discussion and analysis (MD&A), director’s or board’s report, auditor’s report, and the like.
Presentations to investors include facts about the company, growth opportunities, industry analysis, management team, overall performance, innovations, future plans and more. Of course, not every company offers these things to its shareholders.
3. Company or asset growth in 3 and 5 year periods
In fundamental analysis, we always consider the long-term growth of stocks, currencies or assets. For example, time frames of 3 to 5 years are very useful. If the asset has sometimes experienced a drop in price over a period of three or five years, but generally has an upward growth, it will be a good asset.
4. Financial Ratio
Financial ratios are useful in determining a company’s performance and help analyze a company’s competitive position.
Some important financial ratios are:
- Profitability ratios: including profit margin after tax (PAT), return on equity (ROE), return on assets (ROA), return on capital employed (ROCE)
- Leverage ratios: including debt to equity ratio, interest coverage rate
- Operating ratios: including capital turnover, total asset turnover
- Valuation ratios: including price-to-earnings ratio (P/E), price-to-sales ratio (P/S), ratio of enterprise value to earnings before interest, taxes and depreciation (EV/EBITDA)
Two very important approaches in fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis has two important approaches, which are known as top-down approach (whole to part) and bottom-up approach (part to whole). We will explain both below.
Top-down approach
The top-down approach examines macroeconomic factors first and then focuses on the specific company or asset.
In this approach, we first examine the overall health of the company and evaluate various macroeconomic elements such as interest rates, inflation, and GDP levels. After analyzing these factors, industries and sectors that are better opportunities for investment are identified.
Next, we select high-quality assets that have high growth potential but are undervalued. For this purpose, it is sufficient to compare the current price of the property in question with its estimated intrinsic value.
Bottom up approach
In this approach, we first analyze the company and its assets and then examine the impact of macroeconomic factors. This method assumes that the asset or company itself is more efficient than the entire industry.
For this purpose, we first evaluate the currency, stock or asset we want. What is its market value? Is it overvalued or undervalued? Once we’ve chosen the best asset, we look at the company, then the industry as a whole, and finally the impact of macroeconomic factors.
Quantifying the intrinsic value of an asset and comparing it to the current market price can help make investment decisions.
The importance of fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis is an important part of investing and trading. For assets such as currency and stocks and bonds, this type of analysis helps determine the fair value of the asset. About the company, fundamental analysis evaluates the health and performance of the organization with its finances and economic indicators.
With the help of fundamental analysis, it is possible to predict the future movements of the asset price and determine whether its value is undervalued or overvalued.
Advantages of fundamental analysis
Some of the advantages of fundamental analysis are:
- It is suitable for a long-term approach in investment
- With fundamental analysis, you get information about where and when to invest to earn high income in a long-term period
- Fundamental analysis includes both qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis. As a result, it provides a complete insight into the performance of the company or asset.
Disadvantages of fundamental analysis
- This analysis is a time-consuming process that requires multiple areas of analysis, making it a complex process.
- The quantitative type of this analysis is subjective; Because data is not measurable.
Comparison of technical analysis with fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis is the opposite of technical analysis; That is, fundamental analysis deals with a company’s finances, external events, the impact of various factors and industry trends, but technical analysis extracts information from charts. Fundamental analysis is used for long-term investments, but technical analysis is usually used for trading.
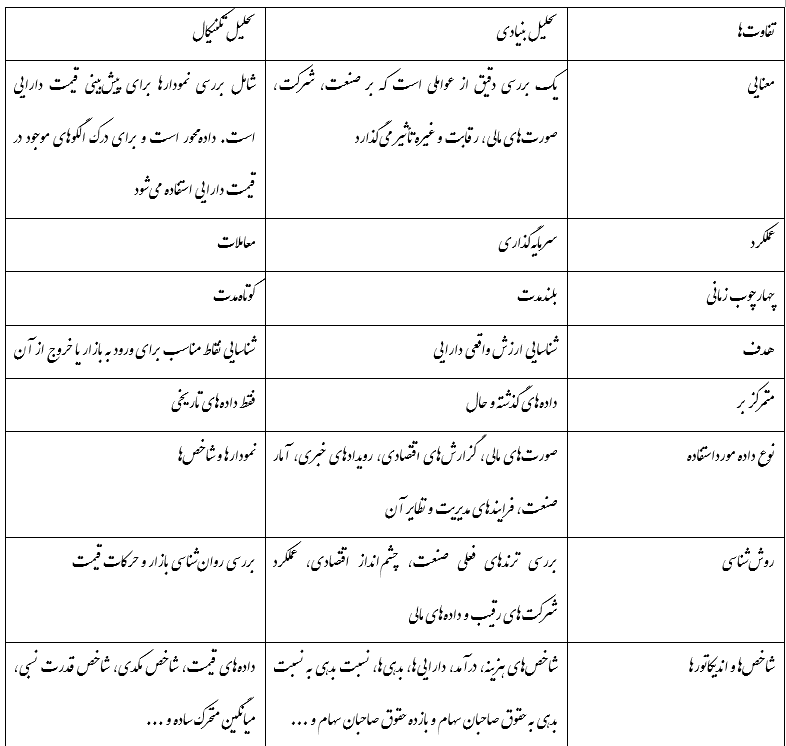
Comparison of technical analysis with fundamental analysis
Who should use fundamental analysis?
Fundamental analysis is useful for many investors and traders; However, it is most essential for two categories of people:
- Long-term investors: This analysis helps them find the asset’s fundamental value and growth potential, establish pricing targets, and ascertain whether the asset is worth the price they are paying.
- Company managers and accountants: These people use fundamental analysis to measure and improve the profitability of an organization by simplifying its operations. This analysis helps them understand where they stand against their competitors.
Conclusion
Fundamental analysis helps predict long-term trends in the market. This type of analysis is often used for long-term investments and helps us understand the intrinsic value of assets such as currency, stocks, and securities by examining micro and macroeconomic factors. With this analysis, we can find good companies to invest in that have strong growth potential.


