Risk management in the forex market
Introduction:
Forex market or currency exchange market is a global and decentralized market where different currencies are exchanged with each other. The forex market is attractive to investors, traders, banks and other market players due to its long working hours (24 hours a day and five days a week), high price volatility, easy access and low costs.
Definition of risk in the forex market:
Risk in the forex market is the probability of an adverse event that will lead to financial loss or loss of profitability.
Risk in the forex market is influenced by various factors such as price fluctuations, interest rate changes, supply and demand level changes, economic and political policy changes, natural disasters and human errors.
Therefore, in order to maintain profitability and reduce risks in the forex market, it is necessary for investors and traders to use appropriate risk management methods. Risk management in the forex market refers to activities that are carried out in order to identify, measure, control and reduce existing or potential risks in the forex market. Risk management in the forex market can be done quantitatively (using mathematical and statistical methods) or qualitatively (using technical and fundamental analysis).
The purpose of this article is to examine the importance, types and methods of risk management in the forex market. In the next section, we will introduce and explain the types of forex market risks and their management methods. In the last part, the conclusion, we will provide a summary of the main points of the article and suggestions for improving performance in the forex market.
Types of Forex market risks
Forex market risks can be divided into several categories. Here, we will examine five common and important types:
– Market risk:
Market risk is the risk caused by currency price changes. This type of risk depends on various economic factors such as inflation, gross domestic product, interest rate, balance of trade and balance of payments. Market risk is usually measured using market sensitive indicators such as exchange rate, Relative Strength Index (RSI), Money Flow Index (MFI) and Average Movement Index (ADX).
– Profitable risk:
It is called the risk caused by changes in the profitable level. This type of risk depends on the trader’s performance and the strategies they use. Profitable risk is usually calculated using indicators related to profitability, such as profit-to-loss ratio (P/L ratio), profit-to-trading volume ratio (P/V ratio), profit-to-account ratio (P/A ratio) and profit-to-risk ratio. P/R ratio) is measured.
– Credit risk:
Credit risk is the risk caused by the inability of one party to fulfill its obligations towards the other party in the forex market. This type of risk depends on the credibility and trust of the transaction parties. Credit risk is usually measured using credit related indicators such as credit score, default risk rate, delinquency rate and delay rate.
– Technology risk:
Technological risk is the risk caused by technical errors, hardware or software defects, cyber attacks or communication interruptions in the forex market. This type of risk depends on the efficiency and security of technological systems. Technology risk is usually measured using technology-related indicators such as response time, latency time, availability time, and recovery time.
– Legal risk:
It is called the risk caused by non-compliance with laws, regulations, contracts or legal developments in the forex market. This type of risk depends on the laws and regulations of different countries. Legal risk is usually measured using law related indicators such as legal change rate, legal conflict rate, legal enforcement rate and legal compliance rate.
Risk management methods in the forex market
Risk management methods in the forex market can be divided into two general categories: internal methods and external methods. Internal methods are methods that traders do personally to control and reduce their risks. External methods are methods that traders use other tools, systems or services in the forex market to control and reduce their risks. Here are some examples of internal methods:
– Internal methods:
– Determining the limit of loss (stop-loss):
Setting a loss limit is a method that traders set a level before trading, and if the price reaches that level, they will close their trades and exit the market with some loss. This method helps to prevent further loss and preserve the trader’s capital.
The question that arises is; How many percent of your capital can be exposed to risk in each transaction?
In answer to this question, it should be said that there are two different types of risk that should be considered:
- Trading risk: A trader should not risk more than 1% of his total capital.
- Psychological risk: This type of risk depends a lot on the mental ability of the trader, with how much balance he can stick to his trading plan.
To calculate the volume of his transactions, the trader can use special programs for capital management (Money Management). This program automatically calculates the volume of trading “lot sizes”. The figure below shows an example of capital management expert for Metatrader 5. By activating the Buy tick, the default stop loss line is placed below the current price, and you can change the default stop level to the desired price. The capital management expert automatically calculates the trading lot size according to the data you have entered in the expert panel.
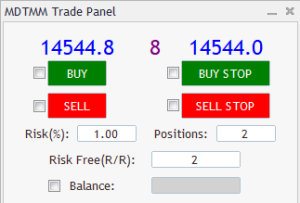
Determining the limit of loss (stop-loss)
– Risk-reward ratio:
Profit-loss ratio is a calculation in which traders determine the ratio of expected profit to their tolerable loss. This method helps to choose profitable strategies. For example, if a trader sets a profit-to-loss ratio of 3 to 1, it means that for every $100 of tolerable loss, he has at least $300 of expected profit.
– Risk diversification:
Risk spreading is a way in which traders choose a basket of currencies or different currency pairs instead of concentrating on a currency pair. This method helps to reduce the risk caused by price fluctuations of a particular currency and increase profitable opportunities.
Conclusion:
The Forex market is an attractive and dynamic market that offers profitable opportunities for investors, traders and other market participants. However, the forex market is also a volatile market that requires careful and regular risk management. Risk in the forex market is affected by various factors such as price fluctuations, interest rate changes, demand and supply level changes, economic and political policy changes, natural disasters and human errors. To reduce and control the risks of the forex market, it is necessary for traders to use appropriate risk management methods. Risk management methods in the forex market include internal methods such as determining the loss limit, the ratio of profit to loss, or risk to reward, and risk spreading. These methods help traders to maintain and increase their profitability as well as reduce and manage potential losses.


